Automation in Food Manufacturing

by Mike Leonard, Publisher, BNP Media
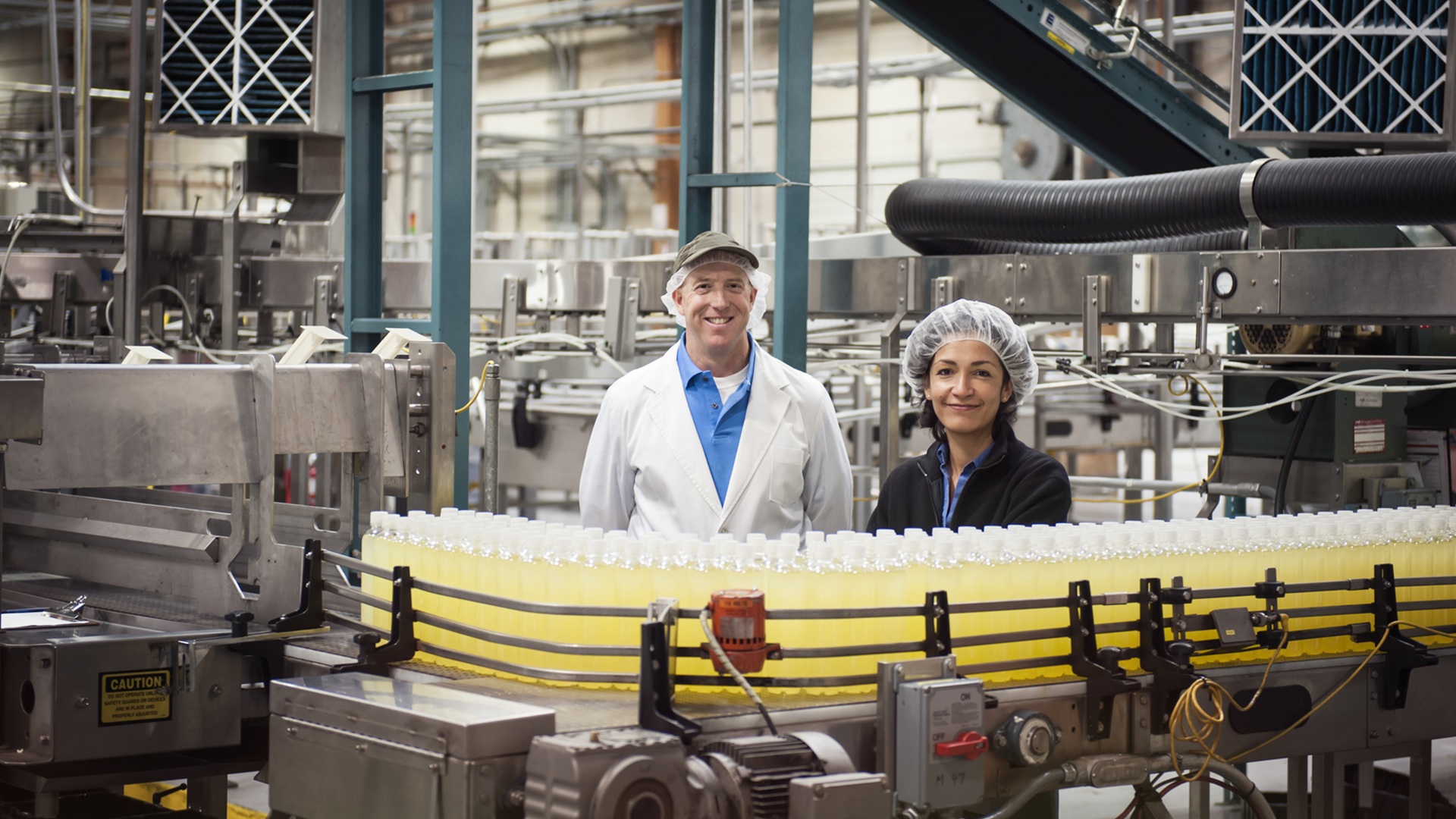
U.S. food processors and manufacturers help feed hundreds of millions of people daily and are increasingly relying on automated technology to achieve safety and efficiencies.
Robotic automation has become pivotal in various stages of food production. For instance, Smithfield Foods utilizes robots to slice hog carcasses, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor-intensive tasks. Similarly, Tyson Foods has invested in robotics and artificial intelligence at its Tyson Manufacturing Automation Center to improve operations in meatpacking, a historically hazardous industry. These robots perform repetitive tasks with high precision and speed, such as sorting, grading, packaging, and palletizing, ensuring consistency and reducing human error. The 2025 FOOD ENGINEERING ranking of top 100 food and beverage companies cited numerous manufacturers pointing to uncertainty in their operating environment, including fluctuating consumer demand, supply chain constraints, extreme weather, high interest rates, tariffs and other trade relations concerns, and political instability and unrest, including the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
The 48th edition of FOOD ENGINEERING’s Plant Construction Survey found food and beverage manufacturers are still cautious when it comes to new projects — because of economic uncertainty connected to inflation and tariffs.
Even with these political and economic concerns, food and beverage manufacturers continue to open and expand manufacturing facilities. FOOD ENGINEERING has reported on more than 30 projects since the start of 2025, nearly all of them with some component of automation. These advancements have not only streamlined operations but also addressed challenges related to labor shortages and skill concerns, food safety and quality control, as well as improving predictive maintenance capabilities.
Cold Chain Concerns
The cold foods manufacturing industry, encompassing refrigerated and frozen food production and temperature-controlled distribution, has undergone a significant transformation through the integration of automation technologies.
Maintaining the integrity of the cold chain is crucial in frozen food production.
Automated systems enhance the efficiency of warehousing activities, including storage, retrieval, and inventory management.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) allow for efficient storage and retrieval of products, maximizing space utilization and reducing the energy required for cooling. Real-time monitoring and data analytics, facilitated by IoT devices, continuously monitor temperature and humidity levels throughout the supply chain, enabling immediate identification and response to any deviations.
Quality assurance in cold food manufacturing has been revolutionized by advanced automated sorting and grading technologies.
Optical sorting machines, equipped with advanced cameras and sensors, detect and remove defective products based on color, shape, size, and even internal defects. This ensures that only the best products reach consumers, maintaining high-quality standards in the industry.
Finally, automated packaging systems and palletizers can increase throughput and order accuracy.